
When evaluating investment properties, understanding vacancy rates is essential. This metric reveals how frequently units remain unoccupied and for how long. It also offers insight into the property’s management efficiency and overall desirability.
For those considering an investment, comparing the property’s vacancy rate to the local market average can help assess its potential profitability. Knowing how to calculate vacancy rates is a valuable tool for making informed decisions.
What Is a Rental Vacancy Rate?
A vacancy rate represents the lost income potential of a property due to unoccupied units. Expressed as a percentage, it indicates the portion of a property that remains unrented over a specific period. Accurately calculating this rate is a key factor in assessing whether a property is a worthwhile investment.
Why Do Vacancy Rates Matter?
Vacancy rates provide insight into both rental income stability and the effectiveness of property management.
- High vacancy rates in areas with strong rental demand could signal management issues or property-related concerns.
- Low vacancy rates may indicate strong demand, competitive pricing, or effective property management.
Investors should analyze these rates to determine if improvements, such as better marketing, renovations, or price adjustments, are necessary to maximize occupancy.
Key Factors Influencing Rental Vacancy Rates
Several elements affect a property’s vacancy rate, including:
- Economic Conditions: High unemployment or slow job growth may reduce rental demand.
- Property Demand: Units that lack modern amenities or desirable features may struggle to attract tenants.
- Rental Competition: An influx of newly developed properties could increase competition and raise vacancy rates.
- Pricing Strategy: Overpricing units compared to market rates can result in prolonged vacancies.
- Property Management: Poor management practices, such as slow maintenance response, can deter long-term tenants.
How to Calculate Vacancy Rates
There are two primary ways to calculate vacancy rates:
- Physical Vacancy Rate
The physical vacancy rate reflects how long a property remains unoccupied relative to its availability. The formula is:
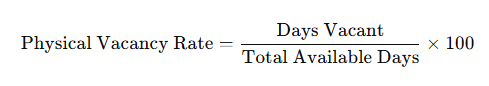
Example:
A single-family rental home is vacant for 90 days out of the 365 days it was available.
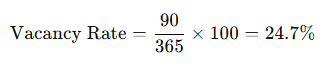
This means the property was unoccupied 24.7% of the time during the year.
- Economic Vacancy Rate
The economic vacancy rate measures the income loss compared to the property’s potential earnings. The formula is:
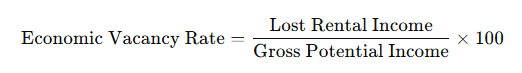
Example:
If a property could generate $2,000 per month but only earns $1,500, the monthly loss is $500.
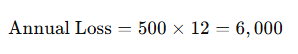
If the potential gross income is $24,000 per year:
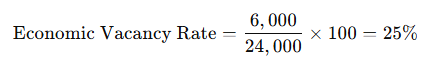
This indicates the property is losing 25% of its potential income due to vacancies or below-market rents.
Average Vacancy Rates: What to Expect
Vacancy rates vary by location and market conditions. For example, the Federal Reserve reported a 5.8% national vacancy rate in 2022, but local rates may differ significantly. Comparing a property’s vacancy rate to the area average can help assess its performance and competitiveness.
Interpreting High vs. Low Vacancy Rates
- High Vacancy Rate: This may indicate ineffective marketing, overpricing, or property condition issues.
- Low Vacancy Rate: Suggests strong demand, effective management, or competitive pricing.
Tips for Reducing Vacancy Rates
To minimize vacancies and increase profitability, property owners can:
- Enhance tenant screening to reduce turnover.
- Invest in marketing to improve visibility and attract quality tenants.
- Upgrade property amenities to remain competitive.
- Adjust rent pricing to match market conditions.
- Maintain the property proactively to retain long-term tenants.
Conclusion
Understanding and calculating vacancy rates is crucial for real estate investors. It reveals both potential income loss and the overall appeal of the property. Monitoring and managing vacancy rates effectively can help optimize profitability and ensure a successful real estate investment.
