
The operating expense ratio (OER), also referred to simply as the expense ratio, is a key metric for property owners and commercial real estate investors. It measures the proportion of a property’s operating costs relative to its income, offering valuable insights into its financial performance.
Why the Operating Expense Ratio Matters
The OER is an essential tool for assessing how efficiently a property generates income in comparison to its operational costs. Investors can use it to evaluate different properties, helping them identify those with better profit potential. It also highlights potential concerns, such as unusually high maintenance costs or poor revenue prospects.
How to Calculate the Operating Expense Ratio
To calculate the OER, subtract depreciation from total operating expenses and divide the result by the property’s gross revenue:
Operating Expense Ratio Formula:
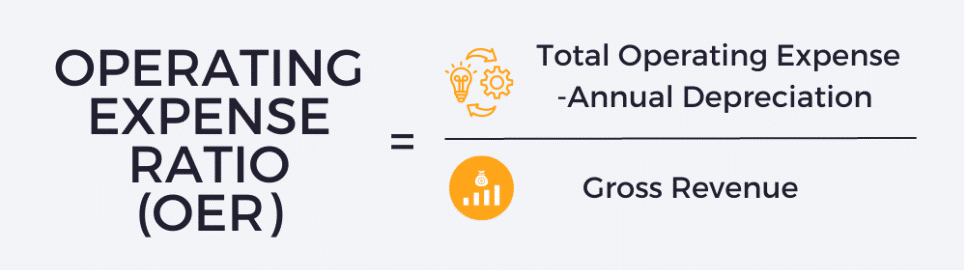
Accurate data is crucial for this calculation, including all ownership and maintenance expenses as well as depreciation, which may vary depending on accounting methods.
Example Calculation
Consider a multifamily property generating $75,000 in monthly rental income, with $50,000 in operating expenses and an annual depreciation of $60,000:
- Annual Expenses: $50,000 × 12 = $600,000
- Adjusted Expenses: $600,000 – $60,000 = $540,000
- Annual Income: $75,000 × 12 = $900,000
- OER: $540,000 ÷ $900,000 = 60%
What Constitutes a Good OER?
A “good” OER depends on property type, market conditions, and individual investor goals:
- Multifamily Properties: Typically between 35% and 45% but can exceed 60% in some markets.
- Office Buildings: Usually ranges from 35% to 55%.
- Retail Properties: Generally falls between 60% and 80%.
- Industrial Properties: Typically lower, around 15% to 25%.
Interpreting High vs. Low OER
A lower OER indicates more efficient operations and greater profit potential, while a higher OER may signal costly maintenance or operational inefficiencies. A high OER can even suggest that expenses outweigh income, making the investment less attractive.
Factors Affecting the OER
The operating expense ratio is influenced by several variables, including:
- Administrative expenses (legal fees, salaries, office expenses)
- Marketing and sales costs
- Utility expenses
- Repairs and maintenance
- Non-capitalized research expenses
In some cases, costs such as direct material expenses, equipment repairs, and labor costs can also impact the OER.
Managing the OER
Effective OER management requires meticulous attention to accurate expense tracking. Debt payments, which are not included in the OER, can sometimes distort comparisons between properties. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence to uncover hidden costs or required upgrades that could impact profitability.
Conclusion
The OER is a valuable metric for evaluating and comparing commercial real estate properties. However, it should be considered alongside other factors to provide a comprehensive understanding of investment potential. Proper due diligence and accurate calculations are crucial for making sound investment decisions.
