
For commercial real estate investors, particularly developers, understanding the floor area ratio (FAR) is crucial. This metric plays a key role in maximizing property usage while adhering to zoning regulations. Below is an overview of what FAR is, how it is calculated, and its significance in commercial development.
What Is Floor Area Ratio (FAR)?
Floor area ratio, commonly referred to as FAR, is a measurement that compares the total building area to the size of the land it occupies. It is a critical factor in urban planning, as zoning laws often impose restrictions on the allowable building density within a given parcel of land. FAR influences building placement, usable space, and overall project feasibility.
Applications of Floor Area Ratio
FAR is widely used in commercial real estate to assess project density. A higher FAR indicates a denser development, which can be beneficial for maximizing land use but must comply with zoning laws. Investors and developers must evaluate FAR early in the planning process to ensure a project’s feasibility within regulatory constraints.
FAR applies to various commercial projects, including office buildings, retail spaces, and multi-family developments. Many municipalities impose FAR limits to manage urban density and maintain infrastructure balance.
Why Is FAR Important for Commercial Properties?
FAR is crucial for several reasons:
- Zoning Compliance: Local laws often set maximum FAR limits, requiring developers to design projects accordingly.
- Property Valuation: Higher FAR zoning typically increases a property’s value due to greater development potential.
- Urban Planning Considerations: High FAR areas can lead to denser buildings, potentially affecting aesthetics, views, and community dynamics.
Investors evaluating land for commercial development must analyze FAR to determine whether the property aligns with their intended project and local regulations.
Understanding Zoning Regulations
Each city establishes zoning regulations that dictate FAR limits, which rarely change without government approval. Developers should consult municipal codes and planning authorities to verify a property’s allowable FAR. Since FAR can differ between adjacent lots, thorough research is necessary before making investment decisions.
How to Calculate Floor Area Ratio
The FAR formula is straightforward and can be calculated manually or with a FAR calculator:
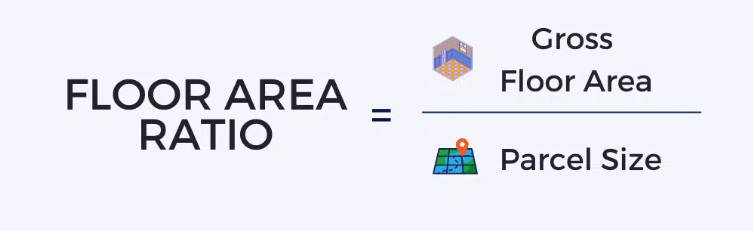
- Gross Floor Area: This includes the total building space measured from the exterior walls, encompassing all floors.
- Parcel Size: The total land area on which the building sits, measured in square feet.
Example Calculation
Consider a building with a total floor area of 10,000 square feet on a 5,000-square-foot lot:
FAR=10,0005,000=2FAR = \frac{10,000}{5,000} = 2FAR=5,00010,000=2
If zoning regulations impose a FAR limit lower than 2, the project may require modifications to meet compliance. In some cases, local authorities may grant exceptions, but approval is not guaranteed.
Conclusion
Before acquiring commercial property, investors should calculate FAR to ensure project feasibility and regulatory compliance. Miscalculating FAR can lead to costly design revisions or project denials. Proper planning and adherence to zoning laws are essential for a smooth development process.
